
Therefore, it is advisable to check different exposure times to achieve an optimum time. Additionally, too high exposure can also lead to this problem. Increasing the washing time can also help to decrease the background. Another problem could be the buffers, which may be too old. (4) High background on the blot: It is often caused by the too high concentration of the antibody, which can bind to PVDF membranes. In this case, use BSA or decrease the amount of milk used. Another reason could be nonfat dry milk masking the antigen. Increasing exposure time can also help to make the band clearer. (3) Faint bands or weak signal: It can be caused by a low concentration of antibody or antigen. If the buffers are contaminated with sodium azide, it can inactivate HRP. It should be ensured that buffers like the transfer buffer, TBST, running buffer, and ECL are all new and noncontaminated. Buffers can also contribute to the problem. Moreover, prolonged washing can also decrease the signal. In this case, an antigen from another source can be used to confirm whether the problem lies with the sample or with other elements, such as the antibody. Another reason for no visible bands is the lowest concentration or absence of the antigen. It is important to remember that some antibodies are not to be used for western blot. Also, the concentration of the antibody should be appropriate as well if the concentration is too low, the signal may not be visible. If an improper antibody is used, either primary or secondary, the band will not show. (2) No bands: This is due to many reasons related to the antibody, antigen, or buffer used. Finally, white (negative) bands on the film are due to too much protein or antibody. To fix this, the gel should be optimized to fit the sample. Nonflat bands can be the result of too fast of travel through the gel, due to low resistance. Also, changing the running buffer can also help the problem. In this case, it should be ensured that the gel is run at a lower voltage and that the transfer sandwich is prepared properly. Similarly, blurry bands are often caused by high voltage or air bubbles present during transfer. If the protein seems to be in too high of a position, then reheating the sample can help to break the quaternary protein structure. It is advisable to use a fresh sample that had been kept on ice or alter the antibody. (1) Unusual or unexpected bands: These can be due to protease degradation, which produces bands at unexpected positions. This paper provides the theoretical explanation of the Western Blotting procedure, troubleshooting tips for common problems: Įven though the procedure for western blot is simple, there could be many unexpected results: Order this positive loading control protein now: Can be used for immuno-precipitation, affinity purification, Western blot and dot blot.Give you confidence in your Western blot protocol.
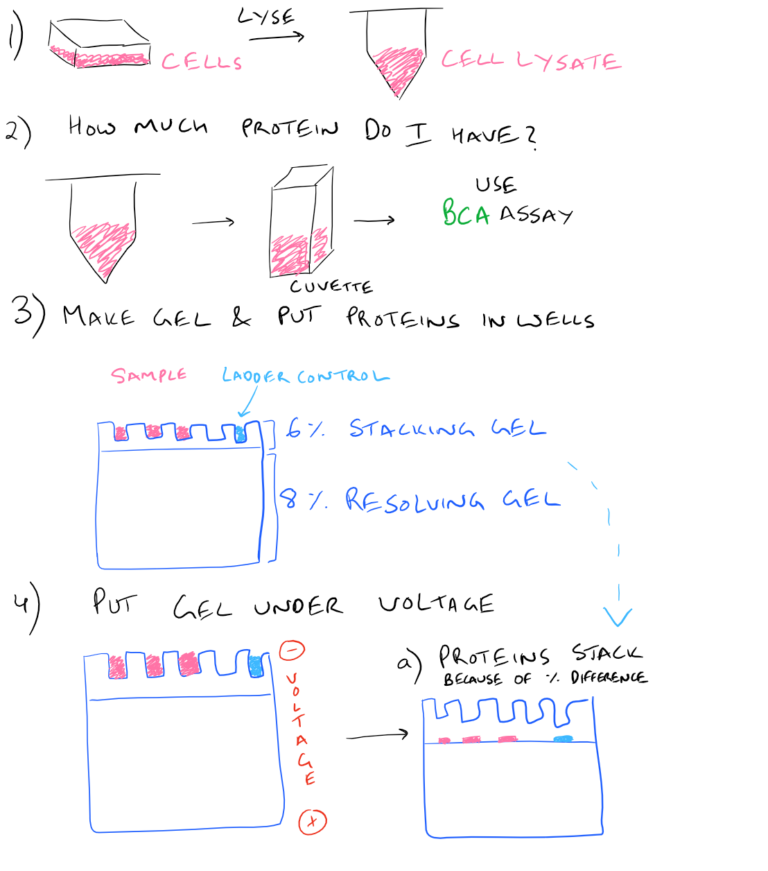
Save time and resources for all your protein research projects.Perfect positive control protein for your Western blotting.Demonstrate that your protocol is efficient and correct.If you detect your protein of interest in the control lane, then an absence of the protein in other lanes is probably directly related to its low abundance rather than a faulty step in the blotting protocol. When trying to detect low-abundance proteins, it is especially important to know that your Western blot is functioning as expected. We strongly recommend the use of a positive control protein when setting up a new experiment this will give you immediate confidence in your Western Blot protocol. It also gives you greater confidence that the results in the other lanes are real rather than artifactual. It means all the steps of your Western blot functioned adequately, including gel electrophoresis, protein transfer to a blotting membrane, membrane blocking, and antibody labeling. Loading such protein into your positive control lane results in a reliably detectable protein sample. The multi-tag positive loading control protein is used to demonstrate that your Western Blot protocol is efficient and correct and that the antibody recognizes the target protein which may not be present in the experimental samples. The bound antibodies are then detected by developing the film. The membrane is then incubated with labels antibodies specific to the protein of interest. The gels are then transferred to a membrane producing a band for each protein. Researchers can identify specific proteins from a complex mixture of proteins extracted from cells using Western Blot.Ī mixture of proteins is separated based on molecular weight through gel electrophoresis. Western blotting is an important technique used in cell and molecular biology. Western Blot: Technique, Theory, and Trouble Shooting


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
